The area now known as Islington was part of the larger manor of Tolentone, which is mentioned in the Domesday Book.

Tolentone was owned by Ranulf brother of Ilger and included all the areas north and east of Canonbury and Holloway Road. The manor house was situated by what is now the east side of Hornsey Road near the junction with Seven Sisters Road.
After the manor decayed, a new manor house was built in 1271 (see below) to the south-east; to differentiate it from the original manor and because it was on a hill, it was called Highbury, from which the area takes its name.
The site for Highbury Manor was possibly used by a Roman garrison as a summer camp . During the construction of a new Highbury House in 1781, tiles were found that could have been Roman or Norman; unfortunately these have been lost.
. During the construction of a new Highbury House in 1781, tiles were found that could have been Roman or Norman; unfortunately these have been lost.
 . During the construction of a new Highbury House in 1781, tiles were found that could have been Roman or Norman; unfortunately these have been lost.
. During the construction of a new Highbury House in 1781, tiles were found that could have been Roman or Norman; unfortunately these have been lost.
Ownership of Highbury eventually passed to Alicia de Barrow, who in 1271 gave it to the Priory of St John of Jerusalem, also known as the Knights Hospitallers in England. The wealthy Lord Prior built Highbury manor as a substantial stone country lodging with a grange and barn.
The wealthy Lord Prior built Highbury manor as a substantial stone country lodging with a grange and barn.
 The wealthy Lord Prior built Highbury manor as a substantial stone country lodging with a grange and barn.
The wealthy Lord Prior built Highbury manor as a substantial stone country lodging with a grange and barn.
In 1381, during the Peasants' Revolt, Jack Straw led a mob of 20,000 rioters who "so offended by the wealth and haughtiness" of the Knights Hospitallers destroyed the manor house. The Lord Prior at the time, Robert Hales, who had taken refuge in the Tower of London, was captured and beheaded on Tower Hill. Jack Straw and some of his followers used the site as a temporary headquarters; consequently the derelict manor became known for the next 500 years as Jack Straw’s Castle. This should not be confused with the better known Jack Straw’s Castle, formerly a pub and now residential flats at Whitestone Ponds, Hampstead, which was named after the semi-legendary leader of the revolt.
John Dawes, a wealthy stockbroker, acquired the site of Jack Straw’s Castle together with 247 acres (1.00 km2) of surrounding land. In 1781 he built Highbury House at a cost of £10,000 on the spot where Highbury Manor had stood. Over the next 30 years the house was extended by new owners, firstly Alexander Aubert  and then John Bentley, to include a large observatory and lavish gardens.The Manor of Highbury remained the possession of the Knights of St John until it was confiscated by Henry VIII in 1540. The land then stayed as crown property until Parliament began selling it in the 17th century.
and then John Bentley, to include a large observatory and lavish gardens.The Manor of Highbury remained the possession of the Knights of St John until it was confiscated by Henry VIII in 1540. The land then stayed as crown property until Parliament began selling it in the 17th century.
 and then John Bentley, to include a large observatory and lavish gardens.The Manor of Highbury remained the possession of the Knights of St John until it was confiscated by Henry VIII in 1540. The land then stayed as crown property until Parliament began selling it in the 17th century.
and then John Bentley, to include a large observatory and lavish gardens.The Manor of Highbury remained the possession of the Knights of St John until it was confiscated by Henry VIII in 1540. The land then stayed as crown property until Parliament began selling it in the 17th century.
The grounds around Highbury House started to be sold off in 1794. By 1894 Highbury House and its remaining grounds became a school. Finally in 1938 Highbury House was demolished and is now the site of Eton House flats (on Leigh Road), built by the Old Etonian Housing Association in 1939.

In 1770 William Willoughby took over Highbury Barn and greatly increased its popularity. He expanded its size and facilities, taking over land and buildings from the farm next door, reaching beyond what is now Kelvin Road and created a bowling green, trap-ballgrounds and gardens. It could cater for company dinners of 2,000 people, concerts and dancing and became one of the most popular venues in London.After the Manor house had been destroyed in 1381, the grange and barn remained on the east side of the track that ran south to Hopping Lane, now St Paul’s Road, roughly on the line of Highbury Park / Highbury Grove (the A1201). In 1740 a small ale and cake house was opened in the Barn, Highbury.
In 1854 events at the annual balls in the grounds of the Barn included the aeronaut Charles Green's  balloon ascent. By 1865 there was a huge dancing platform, a rebuilt theatre, high-wire acts, pantomime, music hall and the original Siamese twins.
balloon ascent. By 1865 there was a huge dancing platform, a rebuilt theatre, high-wire acts, pantomime, music hall and the original Siamese twins. The Barn became the victim of its own success. After a riot led by students from Bart’s Hospital in 1869, locals complained about the Barn’s increasingly riotous and bawdy clientele. This led to a court case and in 1871 authorities revoked the Barn’s dancing licence.
The Barn became the victim of its own success. After a riot led by students from Bart’s Hospital in 1869, locals complained about the Barn’s increasingly riotous and bawdy clientele. This led to a court case and in 1871 authorities revoked the Barn’s dancing licence.
 balloon ascent. By 1865 there was a huge dancing platform, a rebuilt theatre, high-wire acts, pantomime, music hall and the original Siamese twins.
balloon ascent. By 1865 there was a huge dancing platform, a rebuilt theatre, high-wire acts, pantomime, music hall and the original Siamese twins. The Barn became the victim of its own success. After a riot led by students from Bart’s Hospital in 1869, locals complained about the Barn’s increasingly riotous and bawdy clientele. This led to a court case and in 1871 authorities revoked the Barn’s dancing licence.
The Barn became the victim of its own success. After a riot led by students from Bart’s Hospital in 1869, locals complained about the Barn’s increasingly riotous and bawdy clientele. This led to a court case and in 1871 authorities revoked the Barn’s dancing licence.
By 1794 Highbury consisted of Highbury House and Highbury Hill House, Highbury Barn and the gated terraces of Highbury Terrace and Highbury Place, which had been built on land leased by John Dawes. Highbury may have stayed this way, as the plan was to create a 250 acres (1.0 km2) park – Albert Park – between St Paul's Road/Balls Pond Road and the Seven Sisters Road. Instead a 27.5 acre (111,000 m²) site, which is now Highbury Fields was saved in 1869 and the 115 acre (465,000 m²) Finsbury Park were created. The rest of the area was developed.
Instead a 27.5 acre (111,000 m²) site, which is now Highbury Fields was saved in 1869 and the 115 acre (465,000 m²) Finsbury Park were created. The rest of the area was developed.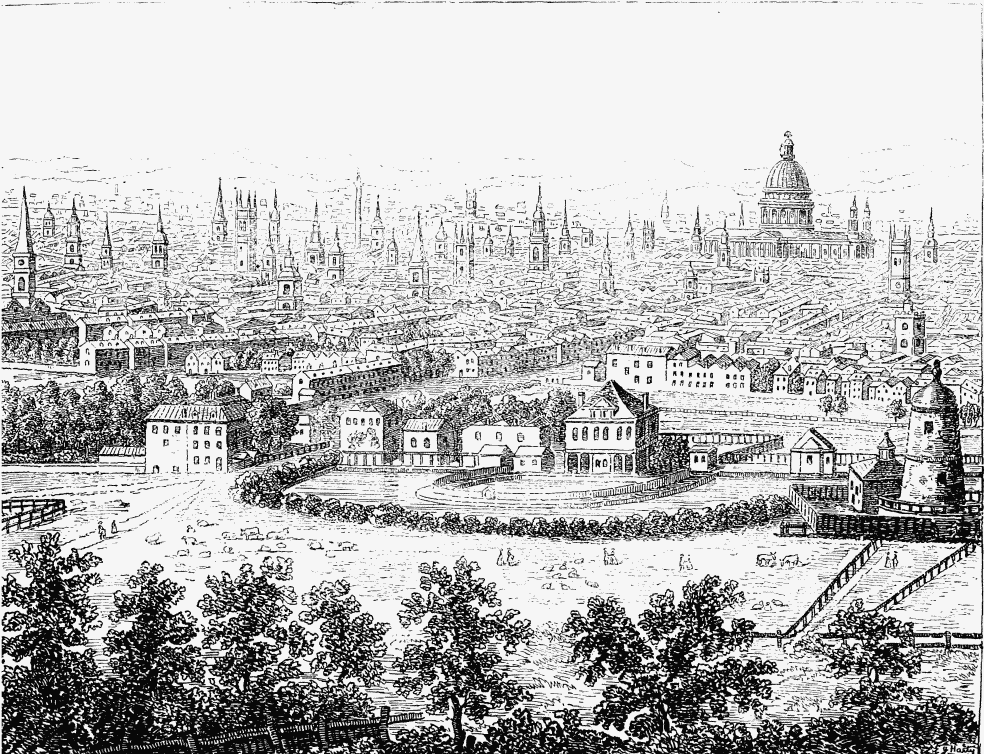
 Instead a 27.5 acre (111,000 m²) site, which is now Highbury Fields was saved in 1869 and the 115 acre (465,000 m²) Finsbury Park were created. The rest of the area was developed.
Instead a 27.5 acre (111,000 m²) site, which is now Highbury Fields was saved in 1869 and the 115 acre (465,000 m²) Finsbury Park were created. The rest of the area was developed.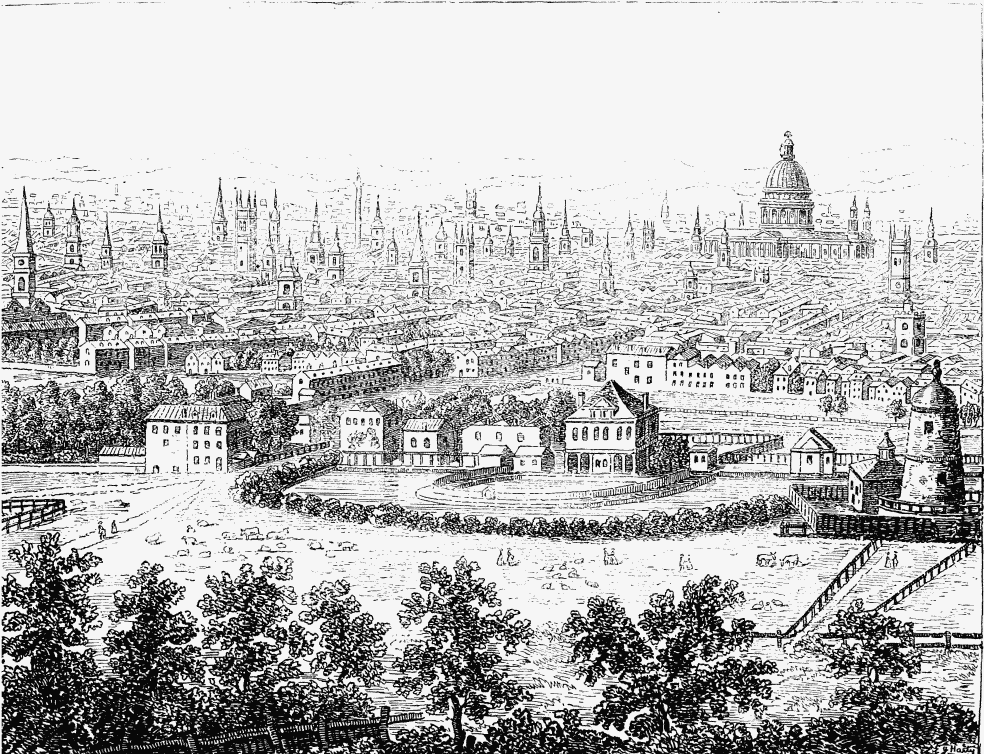
The majority of the development of the area occurred in two phases; until the 1870s many large Italianate villas were built, mostly in the southern part of Highbury.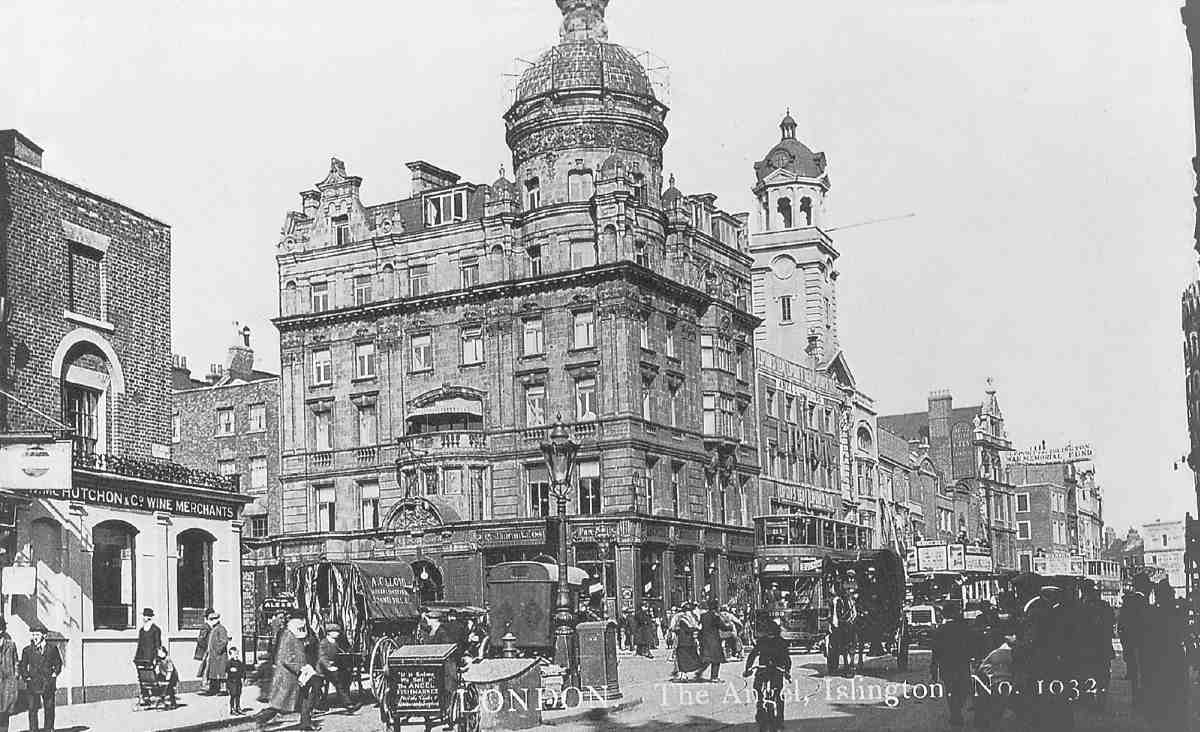  After this time, development went high-density with close packed mostly terraced houses being built, mainly in the north of Highbury. Available land continued to be in-filled with more housing until 1918, but little else changed until after World War
After this time, development went high-density with close packed mostly terraced houses being built, mainly in the north of Highbury. Available land continued to be in-filled with more housing until 1918, but little else changed until after World War 
 After this time, development went high-density with close packed mostly terraced houses being built, mainly in the north of Highbury. Available land continued to be in-filled with more housing until 1918, but little else changed until after World War
After this time, development went high-density with close packed mostly terraced houses being built, mainly in the north of Highbury. Available land continued to be in-filled with more housing until 1918, but little else changed until after World War 
A need for a place for Catholic residents of Highbury to worship in the 1920s led to the commissioning of St Joan of Arc's church, thought to be the first dedicated to the saint canonised in 1920, on a site on Kelross Road where the church hall is now located.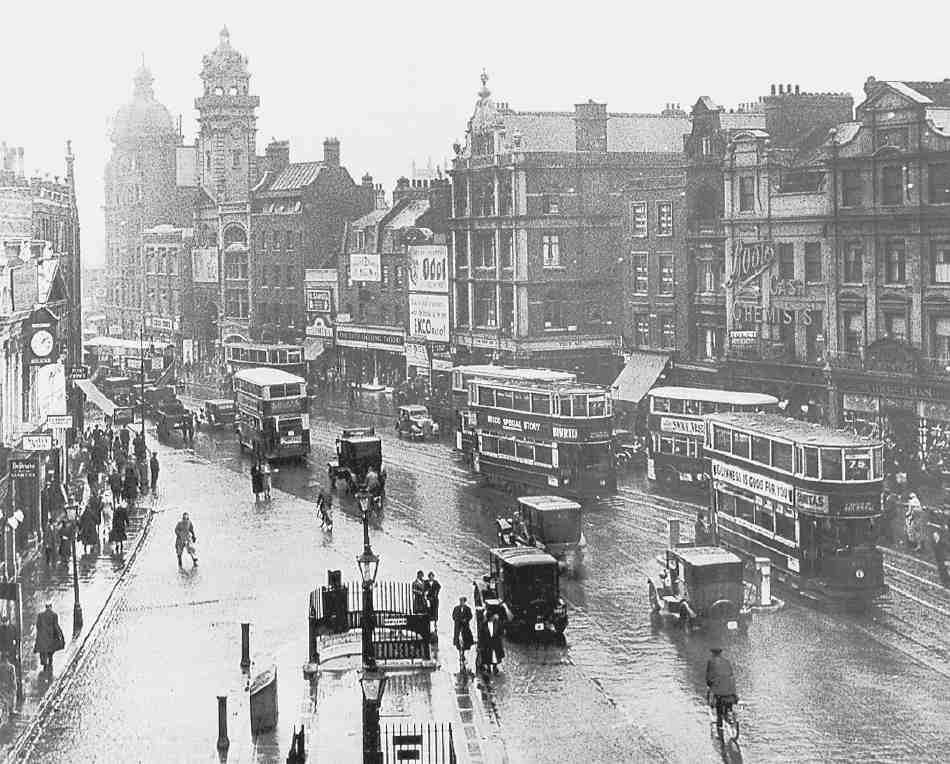 The church was soon expanded, but the influx of Catholic residents after the war led to a need for a new, larger church. The new church, also dedicated to St Joan of Arc, opened on 3 September 1962 on Highbury Park.
The church was soon expanded, but the influx of Catholic residents after the war led to a need for a new, larger church. The new church, also dedicated to St Joan of Arc, opened on 3 September 1962 on Highbury Park.
 The church was soon expanded, but the influx of Catholic residents after the war led to a need for a new, larger church. The new church, also dedicated to St Joan of Arc, opened on 3 September 1962 on Highbury Park.
The church was soon expanded, but the influx of Catholic residents after the war led to a need for a new, larger church. The new church, also dedicated to St Joan of Arc, opened on 3 September 1962 on Highbury Park.
Highbury was bombed during the Blitz and again by V-1 flying bombs. For example, on 27 June 1944, a V-1 destroyed Highbury Corner, killing 26 people and injuring 150.  Highbury Corner had an impressive station and hotel; that was damaged in this attack but its main building remained in use until demolished in the 1960s during the building of the Victoria line.
Highbury Corner had an impressive station and hotel; that was damaged in this attack but its main building remained in use until demolished in the 1960s during the building of the Victoria line. The original westbound platform buildings remain on the opposite side of Holloway Road, as does a small part of the original entrance to the left of the present station entrance. A red plaque mounted on a building wall overlooking the roundabout, commemorates this event.
The original westbound platform buildings remain on the opposite side of Holloway Road, as does a small part of the original entrance to the left of the present station entrance. A red plaque mounted on a building wall overlooking the roundabout, commemorates this event.
 Highbury Corner had an impressive station and hotel; that was damaged in this attack but its main building remained in use until demolished in the 1960s during the building of the Victoria line.
Highbury Corner had an impressive station and hotel; that was damaged in this attack but its main building remained in use until demolished in the 1960s during the building of the Victoria line. The original westbound platform buildings remain on the opposite side of Holloway Road, as does a small part of the original entrance to the left of the present station entrance. A red plaque mounted on a building wall overlooking the roundabout, commemorates this event.
The original westbound platform buildings remain on the opposite side of Holloway Road, as does a small part of the original entrance to the left of the present station entrance. A red plaque mounted on a building wall overlooking the roundabout, commemorates this event.
After the Second World War large-scale rebuilding in parts of Highbury replaced bombed buildings and provided new municipal housing. Some villas that had not been modernised were demolished to make way for yet more municipal housing; some buildings had to be listed to protect them. Following the property boom in the early 1980s, there has been some gentrification in the area[3] and the council has begun selling some of the grand villas to private developers who have the finances to restore them, e.g. in 2004 Islington council sold four buildings on Highbury New Park to developers for £1 million each.

The Highbury Community Association (HCA) was formed in 1997. Since then, the HCA has grown to represent residents and businesses in Highbury, Lower Holloway and Finsbury Park. The HCA campaigns on many different aspects of living and working in this area of North Islington in London.
For 40 years from 1965, Highbury New Park was home to Wessex Studios. Created by Beatles producer Sir George Martin (who grew up on Drayton Park in Highbury), the studios saw the recording of some of the best-known albums created by bands including Queen, Genesis, the Rolling Stones, the Sex Pistols and the Clash.
the studios saw the recording of some of the best-known albums created by bands including Queen, Genesis, the Rolling Stones, the Sex Pistols and the Clash.
The building is now a block of residential apartments called "The Recording Studio" and located at 106, Highbury New Park. 
Highbury was also home to Highbury Studios a film/TV/recording studio further along the same street, at 65A Highbury New Park; these studios had a training school next door in a disused church hall. Built initially as a music conservatoire in 1890, the site became a recording studio in 1926 for the Piccadilly label. In 1933, they became the Highbury (film) Studios and in 1945 they were acquired by the Rank Organisation. Due to economic difficulties, Rank closed the studios down and they were demolished in 1960. Athenaeum Court, a block of flats, now occupies the site.
No comments:
Post a Comment