Odilon Redon was born in Bordeaux, Aquitaine,  a prosperous family. The young Bertrand-Jean Redon acquired the nickname "Odilon" from his mother, Odile. Redon started drawing as a child, and at the age of ten he was awarded a drawing prize at school.
a prosperous family. The young Bertrand-Jean Redon acquired the nickname "Odilon" from his mother, Odile. Redon started drawing as a child, and at the age of ten he was awarded a drawing prize at school. Aged fifteen, he began the formal study of drawing, but on the insistence of his father he changed to
Aged fifteen, he began the formal study of drawing, but on the insistence of his father he changed to  architecture. His failure to pass the entrance exams at Paris’ École des Beaux-Arts
architecture. His failure to pass the entrance exams at Paris’ École des Beaux-Arts  any plans for a career as an architect, although he briefly studied painting there under Jean-Léon Gérôme
any plans for a career as an architect, although he briefly studied painting there under Jean-Léon Gérôme in 1864. (His younger brother Gaston Redon would become a noted architect.)
in 1864. (His younger brother Gaston Redon would become a noted architect.)
Back home in his native Bordeaux, he took up sculpture, and Bresdin instructed him in etching and lithography. His artistic career was interrupted in 1870 when he joined the army to serve in the Franco-Prussian War.
Bresdin instructed him in etching and lithography. His artistic career was interrupted in 1870 when he joined the army to serve in the Franco-Prussian War.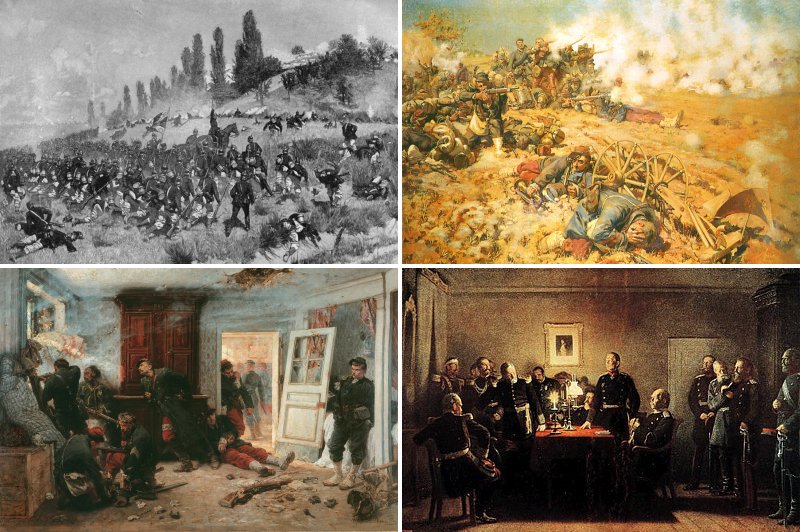
At the end of the war, he moved to Paris, working almost exclusively in charcoal and lithography.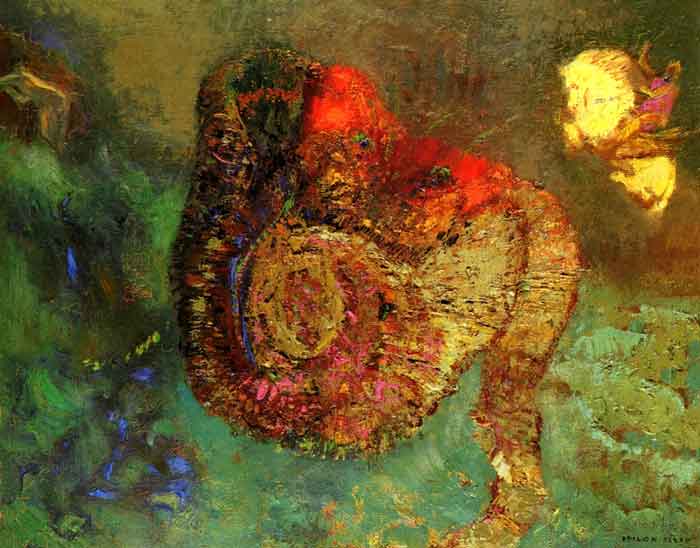 He called his visionary works, conceived in shades of black, his noirs. It would not be until 1878 that his
He called his visionary works, conceived in shades of black, his noirs. It would not be until 1878 that his 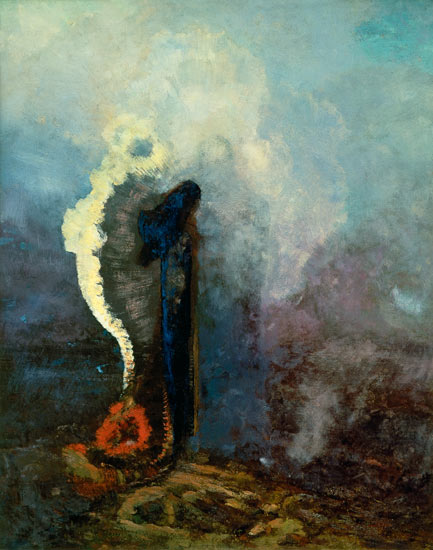 work gained any recognition with Guardian Spirit of the Waters, and he published his first album of lithographs, titled Dans le Rêve, in 1879
work gained any recognition with Guardian Spirit of the Waters, and he published his first album of lithographs, titled Dans le Rêve, in 1879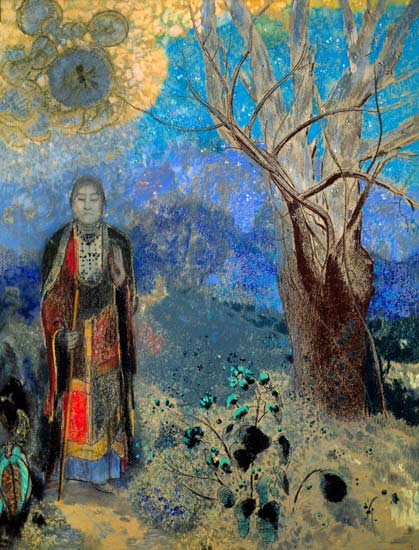 . Still, Redon remained relatively unknown until the appearance in 1884 of a cult novel by
. Still, Redon remained relatively unknown until the appearance in 1884 of a cult novel by  -Karl Huysmans titled À rebours (Against Nature)
-Karl Huysmans titled À rebours (Against Nature) . The story featured a decadent aristocrat who collected Redon's drawings.
. The story featured a decadent aristocrat who collected Redon's drawings.
In the 1890s, pastel and oils became his favored media, and he produced no more noirs after 1900. In 1899, he exhibited with the at Durand-Ruel's
at Durand-Ruel's . In 1903 he was awarded the Legion of Honor.His popularity increased when a catalogue of etchings and lithographs was published by André Mellerio in 1913 and that
. In 1903 he was awarded the Legion of Honor.His popularity increased when a catalogue of etchings and lithographs was published by André Mellerio in 1913 and that same year, he was given the largest single representation at the New York Armory Show
same year, he was given the largest single representation at the New York Armory Show .
.
Redon died on July 6, 1916. In 1923 Mellerio published Odilon Redon: Peintre Dessinateur et Graveur. An archive of Mellerio's papers is held by the Ryerson & Burnham Libraries at the Art Institute of Chicago
An archive of Mellerio's papers is held by the Ryerson & Burnham Libraries at the Art Institute of Chicago .
.
In 2005 the Museum of Modern Art launched an exhibition entitled "Beyond The Visible", a verview of Redon's work showcasing more than 100 paintings, drawings, prints and books from The Ian Woodner Family Collection. The exhibition ran from October 30, 2005 to January 23, 2006.
verview of Redon's work showcasing more than 100 paintings, drawings, prints and books from The Ian Woodner Family Collection. The exhibition ran from October 30, 2005 to January 23, 2006.


"I have often, as an exercise and as a sustenance, painted before an object down to the smallest accidents of its visual appearance; but the day left me sad and with an unsatiated thirst. The next day I let the other source run, that of imagination, through the recollection of the forms and I was then reassured and appeased
 a prosperous family. The young Bertrand-Jean Redon acquired the nickname "Odilon" from his mother, Odile. Redon started drawing as a child, and at the age of ten he was awarded a drawing prize at school.
a prosperous family. The young Bertrand-Jean Redon acquired the nickname "Odilon" from his mother, Odile. Redon started drawing as a child, and at the age of ten he was awarded a drawing prize at school. Aged fifteen, he began the formal study of drawing, but on the insistence of his father he changed to
Aged fifteen, he began the formal study of drawing, but on the insistence of his father he changed to  architecture. His failure to pass the entrance exams at Paris’ École des Beaux-Arts
architecture. His failure to pass the entrance exams at Paris’ École des Beaux-Arts  any plans for a career as an architect, although he briefly studied painting there under Jean-Léon Gérôme
any plans for a career as an architect, although he briefly studied painting there under Jean-Léon Gérôme in 1864. (His younger brother Gaston Redon would become a noted architect.)
in 1864. (His younger brother Gaston Redon would become a noted architect.)Back home in his native Bordeaux, he took up sculpture, and
 Bresdin instructed him in etching and lithography. His artistic career was interrupted in 1870 when he joined the army to serve in the Franco-Prussian War.
Bresdin instructed him in etching and lithography. His artistic career was interrupted in 1870 when he joined the army to serve in the Franco-Prussian War.
At the end of the war, he moved to Paris, working almost exclusively in charcoal and lithography.
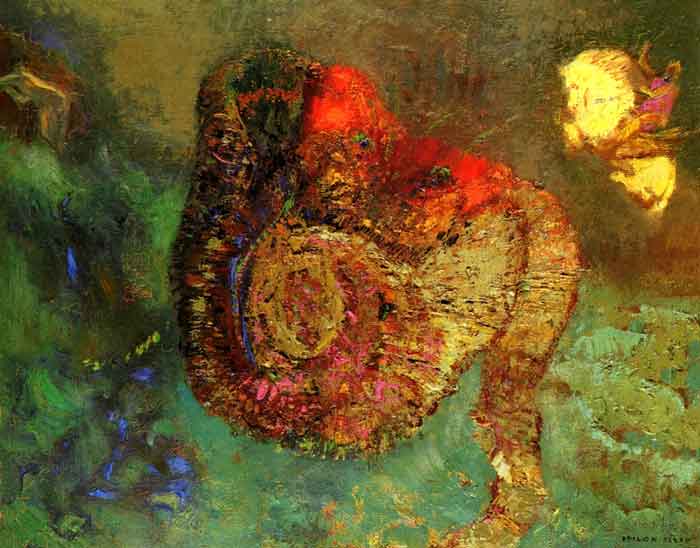 He called his visionary works, conceived in shades of black, his noirs. It would not be until 1878 that his
He called his visionary works, conceived in shades of black, his noirs. It would not be until 1878 that his 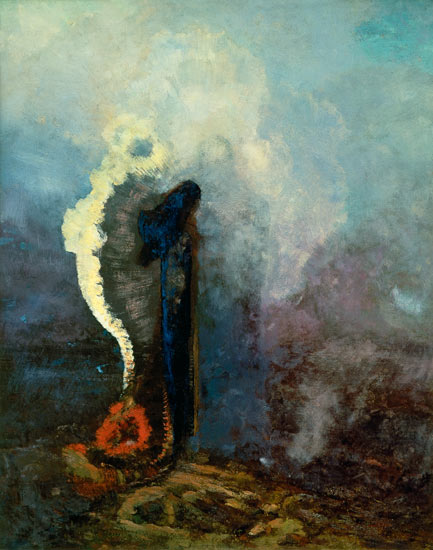 work gained any recognition with Guardian Spirit of the Waters, and he published his first album of lithographs, titled Dans le Rêve, in 1879
work gained any recognition with Guardian Spirit of the Waters, and he published his first album of lithographs, titled Dans le Rêve, in 1879 . Still, Redon remained relatively unknown until the appearance in 1884 of a cult novel by
. Still, Redon remained relatively unknown until the appearance in 1884 of a cult novel by  -Karl Huysmans titled À rebours (Against Nature)
-Karl Huysmans titled À rebours (Against Nature) . The story featured a decadent aristocrat who collected Redon's drawings.
. The story featured a decadent aristocrat who collected Redon's drawings.In the 1890s, pastel and oils became his favored media, and he produced no more noirs after 1900. In 1899, he exhibited with the
 at Durand-Ruel's
at Durand-Ruel's . In 1903 he was awarded the Legion of Honor.His popularity increased when a catalogue of etchings and lithographs was published by André Mellerio in 1913 and that
. In 1903 he was awarded the Legion of Honor.His popularity increased when a catalogue of etchings and lithographs was published by André Mellerio in 1913 and that same year, he was given the largest single representation at the New York Armory Show
same year, he was given the largest single representation at the New York Armory Show .
.Redon died on July 6, 1916. In 1923 Mellerio published Odilon Redon: Peintre Dessinateur et Graveur.
 An archive of Mellerio's papers is held by the Ryerson & Burnham Libraries at the Art Institute of Chicago
An archive of Mellerio's papers is held by the Ryerson & Burnham Libraries at the Art Institute of Chicago .
.In 2005 the Museum of Modern Art launched an exhibition entitled "Beyond The Visible", a
 verview of Redon's work showcasing more than 100 paintings, drawings, prints and books from The Ian Woodner Family Collection. The exhibition ran from October 30, 2005 to January 23, 2006.
verview of Redon's work showcasing more than 100 paintings, drawings, prints and books from The Ian Woodner Family Collection. The exhibition ran from October 30, 2005 to January 23, 2006.The mystery and the evocation of the drawings are described by Huysmans in the following passage:

- "Those were the pictures bearing the signature: Odilon Redon. They held, between their gold-edged frames of unpolished pearwood, undreamed-of images: a Merovingian-type head, resting upon a cup; a bearded man, reminiscent both of a Buddhist priest and a public orator, touching an enormous
 cannon-ball with his finger; a spider with a human face lodged in the centre of its body. Then there were charcoal sketches which delved even deeper into the terrors of fever-ridden dreams. Here, on an enormous die, a melancholy eyelid winked; over there stretched dry and arid landscapes, calcinated plains, heaving and quaking ground, where volcanos erupted into rebellious clouds, under foul and murky skies; sometimes the subjects seemed to have been taken from the nightmarish dreams of science, and hark back to prehistoric times; monstrous flora bloomed on the rocks; everywhere, in among the erratic blocks and glacial mud, were figures whose simian appearance—heavy jawbone, protruding brows, receding forehead, and flattened skull top—recalled the ancestral head, the head of the first Quaternary Period, the head of man when he was still fructivorous and without speech, the contemporary of the mammoth, of the rhinoceros with septate nostrils, and of the giant bear. These drawings defied classification; unheeding, for the most part, of the limitations of painting, they ushered in a very special type of the fantastic, one born of sickness and delirium."
cannon-ball with his finger; a spider with a human face lodged in the centre of its body. Then there were charcoal sketches which delved even deeper into the terrors of fever-ridden dreams. Here, on an enormous die, a melancholy eyelid winked; over there stretched dry and arid landscapes, calcinated plains, heaving and quaking ground, where volcanos erupted into rebellious clouds, under foul and murky skies; sometimes the subjects seemed to have been taken from the nightmarish dreams of science, and hark back to prehistoric times; monstrous flora bloomed on the rocks; everywhere, in among the erratic blocks and glacial mud, were figures whose simian appearance—heavy jawbone, protruding brows, receding forehead, and flattened skull top—recalled the ancestral head, the head of the first Quaternary Period, the head of man when he was still fructivorous and without speech, the contemporary of the mammoth, of the rhinoceros with septate nostrils, and of the giant bear. These drawings defied classification; unheeding, for the most part, of the limitations of painting, they ushered in a very special type of the fantastic, one born of sickness and delirium."

- "My drawings inspire, and are not to be defined. They place us, as does music, in the ambiguous realm of the undetermined."
"I have often, as an exercise and as a sustenance, painted before an object down to the smallest accidents of its visual appearance; but the day left me sad and with an unsatiated thirst. The next day I let the other source run, that of imagination, through the recollection of the forms and I was then reassured and appeased


 (March 9, 1923 – February 2, 2010) was a populist American political writer, biographer, and antisemite.
(March 9, 1923 – February 2, 2010) was a populist American political writer, biographer, and antisemite. in 1391, the persecutions of the Spanish Inquisition, the expulsion from Spain in 1492, Cossack massacres in Ukraine, various pogroms in Russia, the Dreyfus affair
in 1391, the persecutions of the Spanish Inquisition, the expulsion from Spain in 1492, Cossack massacres in Ukraine, various pogroms in Russia, the Dreyfus affair , the Final Solution by Hitler's Germany, official Soviet anti-Jewish policies and the Jewish exodus from Arab and Muslim countries.
, the Final Solution by Hitler's Germany, official Soviet anti-Jewish policies and the Jewish exodus from Arab and Muslim countries.
 Emil Fackenheim supported the unhyphenated spelling, in order to "dispel the notion that there is an entity 'Semitism' which 'anti-Semitism' opposes.
Emil Fackenheim supported the unhyphenated spelling, in order to "dispel the notion that there is an entity 'Semitism' which 'anti-Semitism' opposes. the third child of Eustace Clarence Mullins (1899–1961) and his wife Jane Katherine Muse (1897–1971). His father was a salesman in a retail clothing store.
the third child of Eustace Clarence Mullins (1899–1961) and his wife Jane Katherine Muse (1897–1971). His father was a salesman in a retail clothing store. he enlisted in the military as a Warrant Officer. He was a veteran of the United States Army Air Forces, with thirty-eight months active service during World War II.
he enlisted in the military as a Warrant Officer. He was a veteran of the United States Army Air Forces, with thirty-eight months active service during World War II. during his period of incarceration in St. Elizabeths Hospital for the Mentally Ill
during his period of incarceration in St. Elizabeths Hospital for the Mentally Ill in Washington, D.C. between 1946 and 1959. According to Mullins it was Pound who set him on the course of research that led to his writing The Secrets of The Federal Reserve
in Washington, D.C. between 1946 and 1959. According to Mullins it was Pound who set him on the course of research that led to his writing The Secrets of The Federal Reserve Virginia, in the house on Madison Place where he grew up, from the mid 1970s through the end of his life.
Virginia, in the house on Madison Place where he grew up, from the mid 1970s through the end of his life.


 who he claimed financed them to build up the Nazi war machine, as well as the leaders of the J. Henry Schroeder Bank, who were facilitated by the Dulles brothers, and that Nazi opposition to these bankers, insofar as it went beyond rhetoric, occurred only well after they had ascended to power.
who he claimed financed them to build up the Nazi war machine, as well as the leaders of the J. Henry Schroeder Bank, who were facilitated by the Dulles brothers, and that Nazi opposition to these bankers, insofar as it went beyond rhetoric, occurred only well after they had ascended to power. to World War I.
to World War I. , Bernard Baruch,
, Bernard Baruch, Eugene Meyer
Eugene Meyer , and to a lesser extent, the leaders of Morgan banks, in the United States, and men like Max Warburg in Germany, so that they might increase their profit and power. He also claimed that these individuals would play a key role in financing the Bolshevik Revolution.
, and to a lesser extent, the leaders of Morgan banks, in the United States, and men like Max Warburg in Germany, so that they might increase their profit and power. He also claimed that these individuals would play a key role in financing the Bolshevik Revolution.
 and Arnold Toynbee (who he said was a ripoff of Spengler and a "shabbez-goi historian"), and proposed that if we look at society as if it were an organism, then the Jews would be equivalent to parasites overtaking that organism. He states that Jews "instinctively" want to control the world. He spent the rest of the book attacking Americans for their supposed docility and subservience to the Jews, and predicting that America would be in total cultural decline by the 1980s.
and Arnold Toynbee (who he said was a ripoff of Spengler and a "shabbez-goi historian"), and proposed that if we look at society as if it were an organism, then the Jews would be equivalent to parasites overtaking that organism. He states that Jews "instinctively" want to control the world. He spent the rest of the book attacking Americans for their supposed docility and subservience to the Jews, and predicting that America would be in total cultural decline by the 1980s. in January 2010, Mullins suffered a stroke. He died on February 2, 2010, aged 86, in Hockley, Texas
in January 2010, Mullins suffered a stroke. He died on February 2, 2010, aged 86, in Hockley, Texas






